Website Audit Checklist for 2023: Do SEO Audit Like a Pro
Some website owners spend lots of time in website designing, content creation and backlink building. They do these works day by day without conducting a website audit.
Actually, a website audit is a recommended digital marketing tactic that uncovers how your website works for you and which areas have room for improvement. It will form an actionable roadmap to implement search engine optimization (SEO), UX and UI changes, or website redesign to better the site’s overall performance.
If you’ve never completed a site audit, or it’s been over 6 months since you have, it’s time to conduct a website audit.
Don’t know where to begin? Here is our complete website audit checklist containing suggestions for the types of things you should be checking and analyzing when looking at your website.
So, without any further ado, let’s dive in!
Contents
What Is a Website Audit?
A website audit is a full analysis of your website that helps you identify where there are points of weakness in your website and how those points hurt your site’s performance.
When you conduct a website audit, you can generate detailed reports which contains a list of action items you can fix on your website — such as broken links, poor site architecture, or long loading time. It is a great way to help you improve your site’s performance and drive more traffic.

Why You Need a Website Audit
1. Measure Website Effectiveness & Performance
It can be easy to get so caught up in creating new contents on your website that you forget to quantify your efforts’ success. From content creating to backlink building, so much time has spent. But, what’s the result?
A website audit is an opportunity to quantify how successful recent marketing strategies have been at driving traffic or conversion to your website. It will provide an accurate picture of overall effectiveness, including conversion, tracking, and other specific goals your company wants to achieve.
2. Improve the User Experience (UX)
The user experience (UX) is how a user interacts with and experiences a website. A website audit can decipher details such as which pages have the highest bounce rate and which pages generate the most traffic and convert the most users? Also, you can find some issues that can easily “destroy” the entire experience. For instance, poor load speed or a site that’s not mobile-friendly can drastically reduce a user’s opinion of a website.
3. Weigh the Potential of Competitors
A website audit can reveal the potential of competitors who are also vying for user attention. Items such as keyword gap analysis or general competitor analysis disclose how similar brands are performing, as well as how your website ranks in comparison. These details help uncover gaps in content and shape potential future strategies that reduce the threat of competition in your space.
21 Steps to Conduct a Complete Website Audit
This checklist is organized in 5 categorizes. You can follow the steps in order to conduct a complete website audit.
- Steps 1-3 are focused on some basic tool setup and getting some baseline data about traffic on your website and your current visibility in organic Google search results.
- Steps 4-7 are focused on technical performance.
- Steps 8-13 are about improving user experience.
- Steps 14–19 are about improving your existing website content and on-page SEO
- Steps 20-21 are focused on off-page SEO.
SEO Tracking & Performance Checks
Step #1: Ensure Your Analytics/Tracking is Set Up
Google Analytics is a critical tool for tracking the results of your digital marketing. But you’d be surprised how often we find that Google Analytics either isn’t installed or isn’t installed properly.
Please check these on your website:
- Is Google Analytics installed?
- Are there any errors?
- Is conversion tracking set up?
- Is Search Console linked with Google Analytics?
Step #2: Accessing Google Search Console
Google’s Search Console is another indispensable tool for auditing your site’s SEO health. Part of your technical SEO audit checklist should be ensuring you can access Search Console correctly.
Go to Google Search Console and ensure that you are logged in to the correct Gmail account for your site. If you already have a Search Console account you’ll find it here, or you can set one up.
Make sure the protocol (“http:” vs. “https:”), subdomain (“www.”), and domain (“example.com”) all match with the live version of the site – this means the right Search Console property is available for the rest of the technical audit checklist.
Step #3: Analyze Your Website Traffic
This step is to understand how your website is performing right now.
Google Analytics provides all sorts of incredible insights about your website visitors – where they come from and how they behave on your website. You can discover what pages get the most view, how long people spend on your website, what countries they come from, what device and browser they are using, how they found your website and even how they navigate through your website.
Moreover, Google Analytics can also give you clues about tracking. You should pay much attention to periods with no sessions, sudden shifts in traffic, and very high/low bounce rates.
Technical SEO Checks
Step #4: Make Sure Google Indexes ONE Version of Your Website
Many website owners don’t realize that it’s possible for search engines to index four different versions of your site. That’s because from a Google crawler’s perspective, these are all different URLs:
- http://example.com
- http://www.example.com
- https://example.com
- https://www.example.com
The different ways to write your URL are seen as separate entities or versions, which can be a problem for building a unified, effective backlink profile or increasing the authority of the website.
To test your current configuration, replace “example.com” in the list above with your root domain, and try typing each of the four variations into your browser. If your configuration is correct, they should all resolve to the same version.
If a version of your site isn’t redirecting properly, no worries. Just 301 redirect it to the version you want to use.
Step #5. Find and Fix Indexing Issues
Finding and fixing any issues with indexing is another important item to check. Indexing is crucial to your page appearing in the search results. If your pages aren’t indexed, they won’t appear in the search results, and it will hurt your SEO.
You can check your index status report in the Google Search Console. In this feature, you will see the number of pages that Google has crawled on your domain. Make a note of any extreme or recent drops in the number of total “Valid” pages. Your technical SEO audit checklist should also note of any spike or large increase of listed “Errors” or pages that are “Valid with warnings”.
List “not found” pages, soft 404s, server errors, or any other issues mentioned by Search Console along with the total number of pages with each issue – these should be priority when you set out to fix your site’s SEO issues.
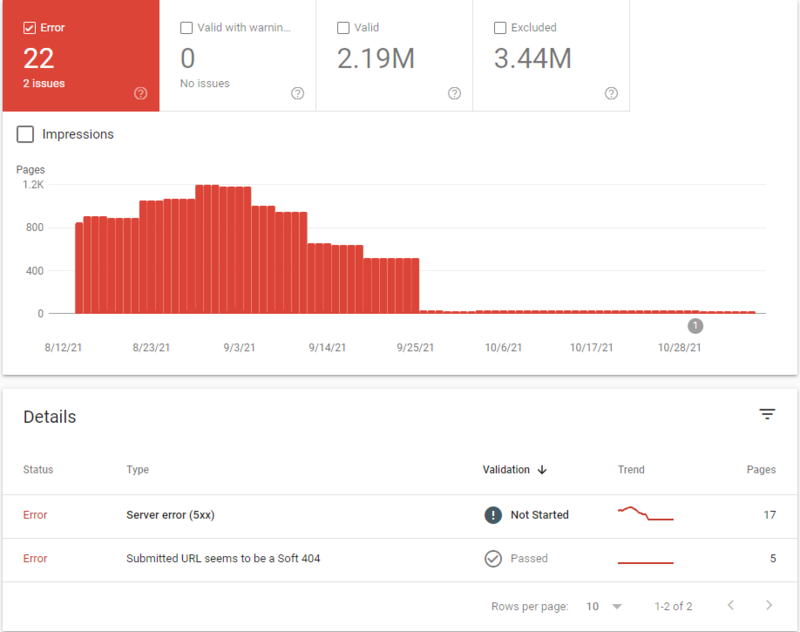
Step #6. Resolve Broken Links (404s)
Broken links might not directly play into the ranking factors of Google’s search engine algorithm, but it can be frustrating for people to click a link on your website and find that it doesn’t take them to the correct or working URL. And that can hurt you when it comes to both bounce rate and your rankings.
You can use Google Search Console to check for broken links. To fix broken links, you should update the target URL or remove the link altogether if it doesn’t exist anymore.
Step #7. Update Your Site Security
To upgrade your site security, ask yourself the following questions and get the “YES” answer:
- Do you have an SSL certificate correctly installed on your website?
- Do you have back-ups enabled on your website?
- Do you know how to access a back-up if there are issues on your website?
- Are your website plugins up-to-date?
- Do you have security and anti-spam measures in place?
- Do you have a strong password for your website admin and hosting logins?
- Does your site use security best practices, like denying access after several failed logins?
User Experience Checks
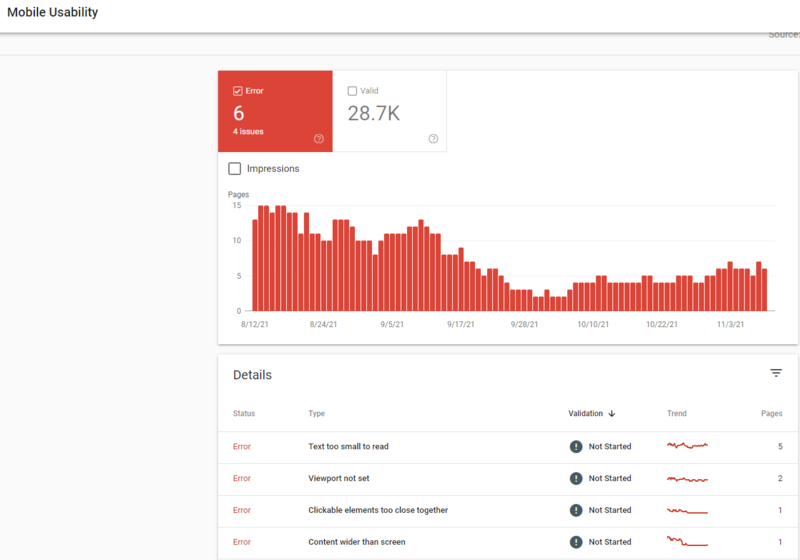
Step #8. Check to See If Your Site Is Mobile-Friendly
Having a mobile-friendly website is absolutely crucial, not only for your Google search ranking (indeed Google now prioritizes how your website looks & functions on mobile over desktop) but for the general user experience of your visitors. Now, over 60% of user are searching via mobile devices.
One of the easiest ways to make your site mobile-friendly is by using a responsive design. A responsive design ensures that your website adapts to whatever device a user is using. Your website will display properly on desktops, mobile devices, and tablets.
Testing if your website is mobile-friendly is just as easy. Head over to Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test, type in your URL and run the test.
When testing your website on mobile phones, please look out for:
- Font sizes – is the copy too small to read? Or is it too large and breaking up over multiple lines?
- Buttons – make sure they’re big enough to press on mobile.
- Layout – are there any elements that are overlapping, making text difficult to read.
- Scrolling – how much scrolling does one have to do on a mobile to get to the main part of the page?
- Page size – the smaller your web page, the quicker the page loads.
Step #9. Improve Page Load Speed
Not only has Google announced that page speed is officially a ranking factor, but it has a big (negative) impact on your conversion rates.
You can use Google PageSpeed Insights to test your site speed. If your site is taking a long time to load, you can follow up these 18 ways to speed up your website.
Having a clean, simple website architecture is important for three reasons:
- It’s easier for users to understand what your website is about and find the content they are looking for.
- It’s easy for search engine crawlers to find all your content and index the website accurately.
- It communicates to Google (and your users) which pages are more or less important.
The same, ask yourself following questions and get the “YES” answer.
- Do the links on your navigation bar make sense?
- How many levels of drop-down menus do you have?
- Are your most important links on the main menu or hidden in a drop-down menu?
- Do you provide quick links in your footer so that your website visitor doesn’t have to scroll all the way back up to the navigation menu?
- For longer pages, do you use jump links that let people jump to different sections on a page?
Step #11. Update Your Page Experience
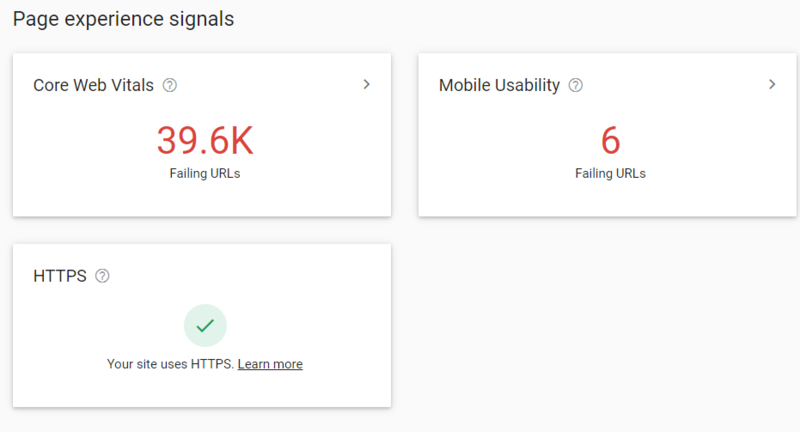
Google’s new page experience signals combine Core Web Vitals with their existing search signals, including mobile-friendliness, safe-browsing, HTTPS-security, and intrusive interstitial guidelines.
Google’s Core Web Vitals are comprised of 3 factors:
- First Input Delay (FID) – FID measures when someone can first interact with the page. To ensure a good user experience, the page should have an FID of less than 100 ms.
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) – LCP measures the loading performance of the largest Contentful element on screen. This should happen within 2.5 seconds to provide a good user experience.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) – This measures the visual stability of elements on screen. Sites should strive for their pages to maintain a CLS of less than 0.1 seconds.
Check these factors on Google Search Console. And if your website currently cannot meet the Google’s standards for the three Core Web Vitals metrics, you can watch the video below to fix Core Web Vitals issues one by one.
Step #12. Check Your Website Against User Accessibility Guidelines
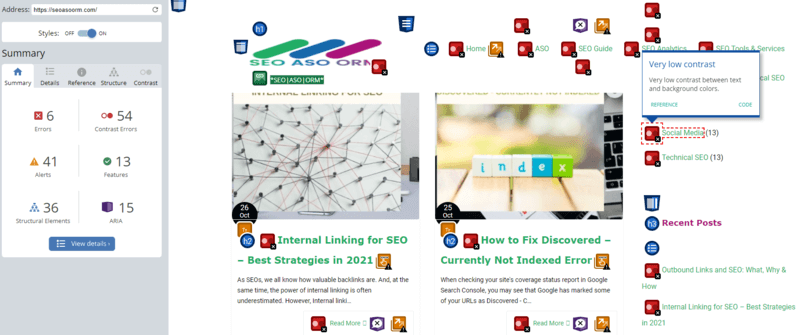
In this step, we’ll use a free tool provided by the WebAIM to check your website against accessibility standards.
Open the WAVE tool from WebAIM and enter a URL from your website. You may need to run the tool on several different pages from your website to make sure all your standard page layouts are set up correctly. Then, you’ll see a report that looks like this:
The panel on the left includes a summary of the errors, warnings and accessibility features the tool identified on the page. You can click into the details tab to view more information about which page elements triggered the different checks.
Step #13. Make Sure Your Website is Functioning Properly
Aside from the technical issues we mentioned above, we’ve come up with another three tips to get you started in the process of making sure your website functions as it should.
- Do your contact forms work? Do you receive an email notification when someone sends a message via your website’s contact form?
- Does the checkout process work – all the way from adding an item to cart to making final payment and receiving confirmation by email.
- Are people able to sign up to your email list and do they receive a welcome email or lead magnet from you upon signing up?
Content & On-Page SEO Checks
Step #14. Get Rid of Any Duplicate or Thin Content
Make sure there’s no duplicate or thin content on your site. Duplicate content can be caused by many factors, including page replication from faceted navigation, having multiple versions of the site live, and scraped or copied content.
Fixing duplicate content can be implemented in the following ways:
- Setting up 301 redirects to the primary version of the URL.
- Implementing no-index or canonical tags on duplicate pages
- Setting the preferred domain in Google Search Console
- Where possible, deleting any duplicate content
Making sure your on-page SEO tags are used appropriately is a very tedious process. That’s because it includes so much, sun as title tags, headings, description tags, and image tags.
You had a 30+ point checklist, and you went through it.
For each page.
Here are what we check for when reviewing these SEO tags and the content of your post.
Title Tags:
- Are your title tags unique on all pages?
- Do your title tags include well-researched keywords?
- Are your title tags well-written (e.g. not over-optimized)?
- Are your title tags the appropriate length? (We aim for 50-65 characters)
Meta Descriptions:
- Do you have unique meta descriptions on all pages?
- Do your meta descriptions contain relevant, engaging copy?
- Are your meta descriptions the appropriate length? (We aim for 120-155 characters)
Header Tags:
- Do you have headers on your webpages?
- Do your headers include relevant keywords, without being over-optimized?
Image Tags:
- Do you have relevant, descriptive keywords in the alt tag?
- Do you have relevant, descriptive keywords in the image file name?
Website Copy:
- Does your website copy incorporate relevant keywords into the body text?
- Do you have sufficient copy on pages you want to rank in Google? We recommend a minimum of 500 -800 words of copy
- Does your website copy satisfy the searcher’s intent?
- Is your website content unique? (We recommend avoiding duplicate content both across your own webpages, as well as between your website’s pages and other webpages on the Internet)
Step #16. Track Your Keyword Rankings
If you have invested the time in doing keyword research and optimizing your website content, you’re probably interested in tracking whether your positions in the Google Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs) is increasing or decreasing.
In fact, reporting on SEO and proving the campaign’s success remains one of the key challenges for SEOs. Well, one way is to show how many keywords have started to rank since your last report, at which positions, and how much traffic and sales those ranking keywords impacted the associated pages. Similarly, you can report on the performance change over time to illustrate your overall progress.
Moreover, tracking keyword rankings can also help you:
- Troubleshoot traffic drops
- Identify new opportunities
- Monitor your competitors
- Identify organic CTR issues
- Identify keyword relevancy
- Identify low-hanging fruit opportunities
Step #17. Analyze Your Internal Links
While internal links may not have the same influence on search rankings as backlinks, they still play a critical role in helping search engines understand the information hierarchy for your website and establishing an SEO-friendly site architecture.
When you audit internal links, there are five things that you need to do:
- Ensure a consistent structure
- Optimize for click depth
- Eliminate orphan pages
- Audit the pagerank flow
- Revise anchor text
- Optimize the number of internal links.
Many internal links are a signal to Google that a specific page is important. You can check how many internal links a page has with Google Search Console’s link tab. It will show all pages in a descending order based on how many internal links they receive.
- Are you giving too many internal links to content targeting low-volume keywords?
- Does your cornerstone content have too few internal links?
These are the questions you want to answer by going through this breakdown.
Step #18. Content Gap Analysis
Content Gap Analysis is the process of comparing the current content offerings with the desired offerings of the audience and attempts to identify what is necessary to fulfill those desires.
The process involves setting concrete goals, profoundly understanding your buyer personas, mapping the buyer’s journey, doing market and competitor research, and conducting an audit of your content assets.
There are two main strains of content gap analysis in SEO.
- Competitor-based content gap analysis
- Market-based content gap analysis
Competitor-based content gap analysis involves:
- Finding out what keywords your page (or entire website if you want a more general overview) ranks for
- Finding out what keywords your competitors’ page ranks for
- Building a list of competitor keywords that you’re NOT ranking for
- Coming up with hypotheses of why your page is not ranking for those terms and putting your theories into action
Market-based content gap analysis involves:
- Getting a crystal clear idea of who your audience is as well as their needs and desires
- Doing keyword research to find what topics and questions are not answered in your article, page, or resource
- Coming up with hypotheses of why your page is not ranking for those terms and putting your theories into action
Step #19. Review Structured Data & Rich Snippets
Structured data is essentially marking up your website’s code to make it more easily readable by search engines. If a website uses structured markup data, Google might display it in SERP as rich snippets which can improve CTR. Here’s an example:
There are many types of structured data that can be applied to web pages (e.g “HowTo”, “FAQ”, “Article”, “Event”, “Job posting”, “Video”, “Course”, “Recipe”, “Review snippet”, or even “Organization” markup).
After you highlight your content using structured data, it is recommended to test it using Google’s own Structured Data Testing Tool. If any errors were uncovered, do whatever you need to do to fix them.
Off-Page SEO Checks
Step #20. Analyze Your Backlinks
Backlinks play a large role in rankings, so we’re also going to have a quick backlink audit.
Here’s what you need to check for when reviewing backlinks:
- How many total referring domains link to your entire website?
- How many backlinks do your content and landing pages have?
- Are you monitoring the growth of your entire link portfolio weekly?
- Is your backlink portfolio growing or shrinking over time?
- Have you used Google Disavow Tool to cut bad backlinks?
- Are your backlinks relevant in terms of their location, language, and focus topic?
Step #21. Check Your Competitors’ Backlink Profiles
Go through the following steps to perform a competitor backlink analysis and create a link building plan for your website.
- Make a list of your competitors
- View your competitor’s backlink profile using Ahrefs (or similar software)
- Find the sites and pages driving the most traffic to your competitors
- Analyze your competitors’ backlinks by backlink quality, backlink placement, and backlink relevance
- Save sites that are good backlink opportunities
Our Website Audit Is Complete!
There you have it!
The best way to get around auditing your website is by using all the aforementioned pointers. It may cost you a lot of time, but these will definitely help you better understand and improve your website.
If you want to make the process easier to manage and complete, you can also take advantage of some website auditing tools, such as Ahrefs and SEMrush. You can use them to keep an eye on your organic keywords, competitor research, and backlinks.