10 Most Important SEO KPIs & Metrics You Should Track
SEO KPIs are values used by marketing teams to measure and understand their search marketing performance. It’s important to measure SEO metrics and track changes day by day or month over month. SEO KPIs help you:
- Demonstrate the value of your SEO to clients (or boss)
- Spot and cut off failing marketing efforts early
- Discover and do more of what works
- Tie your SEO activities to business objectives
But, what’s KPIs we should measure in SEO? In this article, I will look at the most important SEO KPIs (key performance indicators), as well as how to track these KPIs to show them to your client or boss. Or, if you are the client or the boss, you can use these SEO KPIs to measure the true SEO performance.
Let’s dive in.

Contents
10 Vital SEO KPIs to Measure
1. Organic Traffic
One of the main goal of SEO is to get more users from search engines, so the first main KPI you’d want to track is organic traffic.
How to Track it
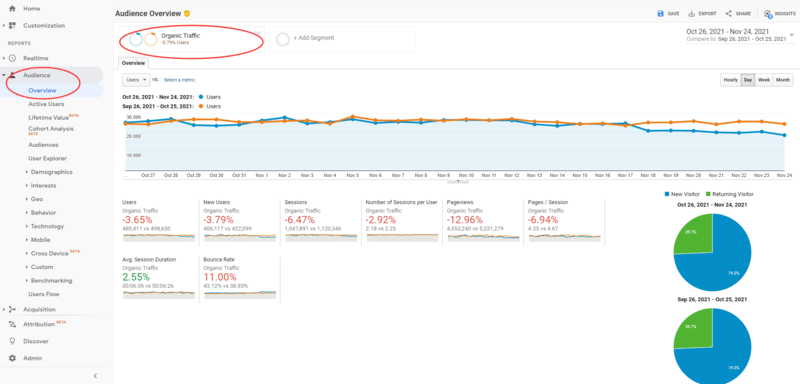
- Log into your Google Analytics dashboard and head over to Audience > Overview
- Click on the ‘Add Segment,’ and select the ‘Organic Traffic’ filed.
- Check Compare to previous period / last year to create a benchmark.
2. Branded vs. Non-Branded Traffic
While focusing on individual queries, analyzing your branded traffic is also important to find the true impact of your SEO efforts.
A branded keyword is a keyword that has your brand’s name included in it, or a variation of your brand’s name in it. If someone were to search that keyword, something related to your brand would pop up, including your website, products, and social media accounts. Non-branded keywords, on the other hand, are keywords that are related to your brand but don’t have your brand’s name in them.
Branded keywords are important because they help more internet users find your business directly. Also, branded keyword searches are high intent and more likely to convert than non-branded keywords.
Non-branded keywords are important because they help you gain visibility online through SEO efforts.
So, when your organic traffic drops or increases, it is important to figure out the performance of branded and non-branded keywords.
How to Track it
You can see all your branded and non-branded queries, their impressions and clicks in Google Search Console. And if you connect your Search Console with Google Analytics, you will have all these stats conveniently laid out there.
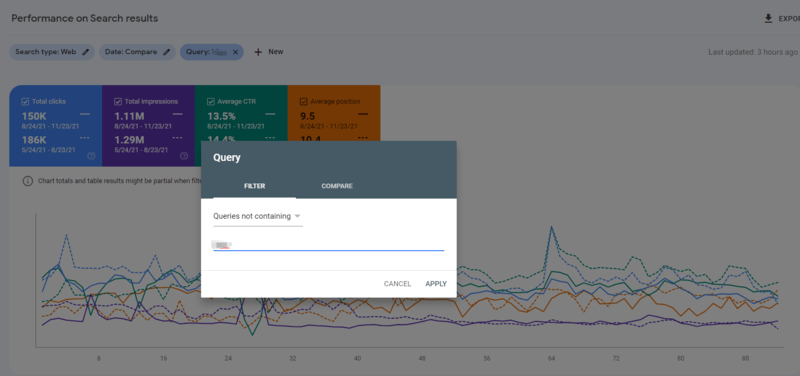
- Access the ‘Performance’ reporting section in GSC from the left-hand navigation.
- Hit the “+ NEW” button to add a new query filter.
- Select “Queries containing” if you want to isolate the performance of branded organic search or “Queries not containing” to isolate non-brand organic search.
- In the blank “Keyword” field, enter several letters that are representative of the most common name of your organization.
- Hit “APPLY” and you’re now viewing only the branded search terms or the non-branded search terms (depending on whether you used “queries containing” or “queries not containing” in your filter in step 3).
- Use “Compare” within your date range filter to view trended performance in your brand or non-brand organic search performance in terms of Clicks and Impressions.
3. Keyword Rankings / Search Ranking
Keyword rankings come into place where the specific keywords that concern your business are positioned in the major search engines like Google or Bing, etc. The higher the positions, the more your pages are noticed in search, the more visitors you get.
In SEO field, keyword ranking is an essential KPI because it’s the first entry point to achieve other primary objectives: more organic traffic, leads, and sales.
How to Track it
You can easily track keywords rankings with some keyword tracking tools. Google Search Console will show you 1,000 keywords. If your website ranks for more than 1,000 keywords, you can use a keyword position tracking tool. Here I take Ahrefs as an example.
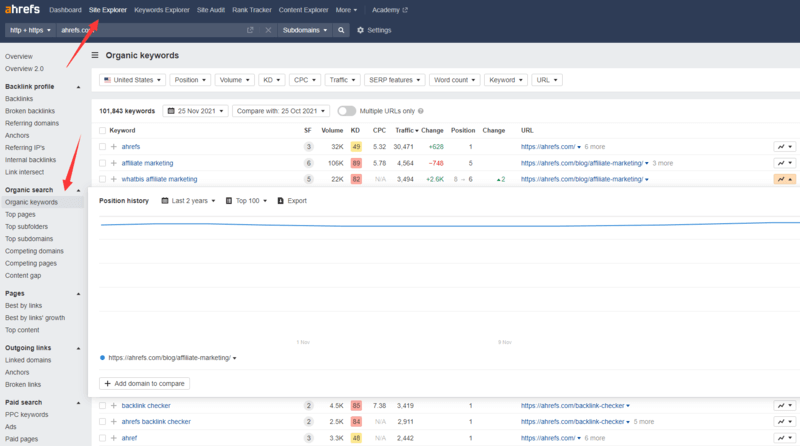
- Enter your website address via Ahrefs > Site Explorer, and then click “Organic Keywords”.
- Ahrefs will automatically detect what keyword your website is ranking for & you can specify ranking based on country.
4. CTR Benchmarks
Measuring your average CTR tells you how good your search engine listings are at generating clicks to your website. It’s measured by the percentage of people that see your site (impressions) in Google and click on the result to visit your site. The higher your CTR, the better. Higher CTR equals more clicks, which equals more traffic.
CTR are affected by many factors.
Keyword rankings directly correlate with Click Through Rate (CTR) – the higher your website ranks, the higher your CTR will be for that keyword. Here’s a breakdown of CTR by ranking position in Google:
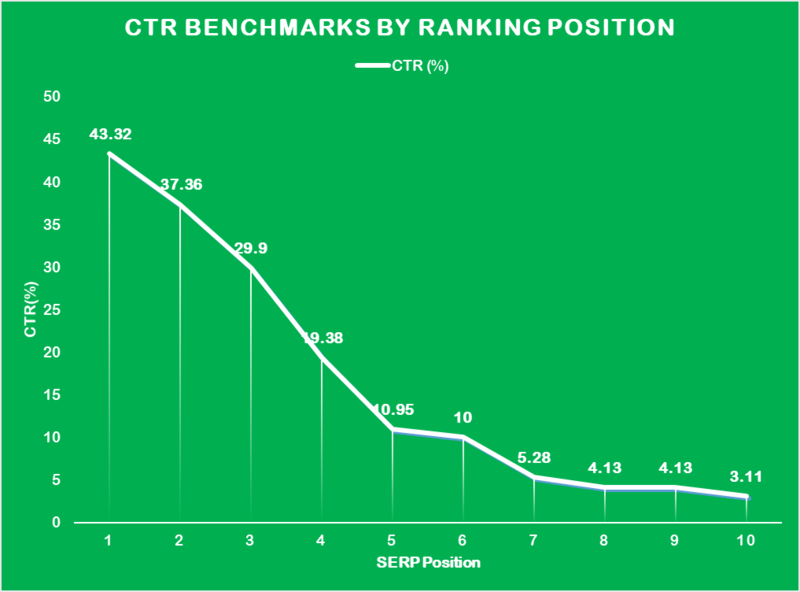
Aside from positions, you should consider the layout of the SERP. Depending on what you see at the top (a featured snippet, a sitelink, or any other rich feature), you might get a different click-through-rate across all positions of the result page.
How to Track it
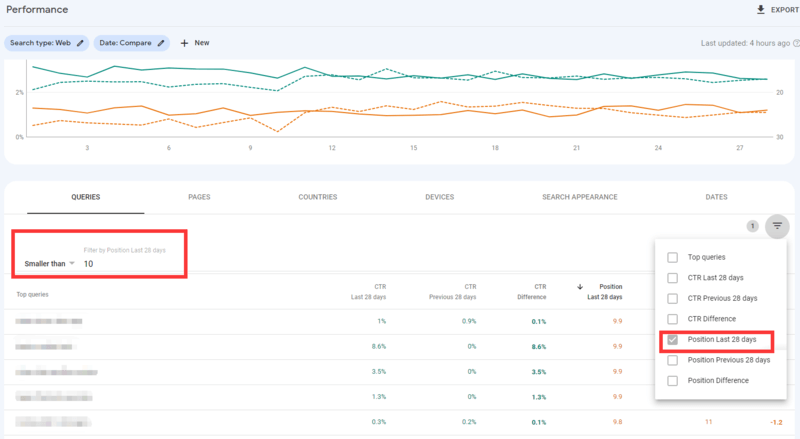
- Log into your Google Search Console dashboard and go to Search Results > Performance. Activate CTR and Average position, deactivate the other two.
- In the table below, use filters to view only the queries for which you rank in positions one through ten. Sort the list by position.
- Scroll through the list and see if any of your pages have a click-through rate lower than what is considered normal for their position in search.
- Once you find a keyword which has low CTR, go visit its SERP, and investigate the reason for poor click-through-rate. Sometimes the CTR is low because there are too many ads and/or knowledge panels stealing your clicks, in which case there is nothing you can do. Other times the CTR is low because your snippet is not attractive enough, in which case you have to optimize your title and description and look into using structured data to enhance your snippet.
5. User Behavior Metrics
User behavior metrics provide valuable insights into the user experience on your website. They show how well (or not), visitors are ‘engaging’ with your content once they arrive on your website.
Bounce rate, session depth, and session duration are all behavioral SEO metrics
- Avg. Session Duration – quite simply, how long someone spends on a specific session. The longer, the better, which indicates the person read the content and spent time with it.
- Page/Session – the average number of pages a person looked at on your website during their session. More pages = more engaged visitor who wants to find out more.
- Bounce Rate – the percentage of visitors that leave a page without taking another action, like clicking on a link, filling out a form, or buying something.
How to Track it
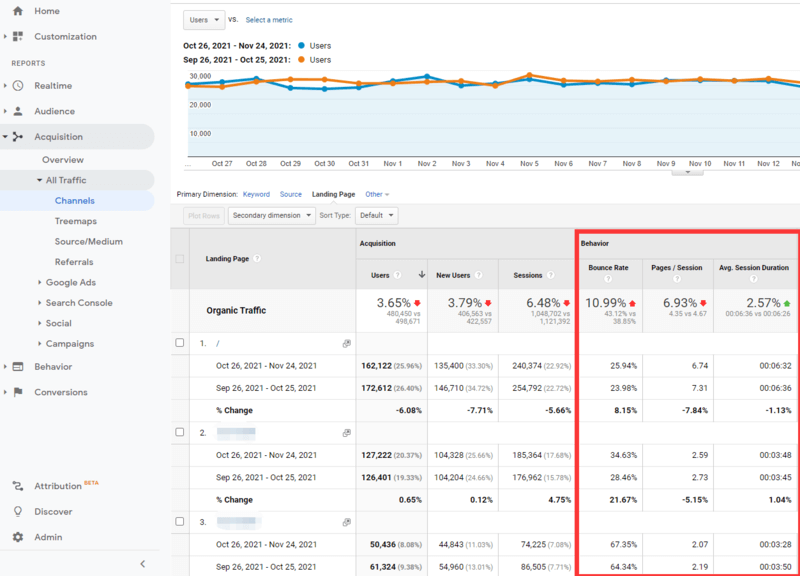
- Log into your Google Analytics account.
- Select Acquisition from the left-hand menu, and then choose All Traffic > Channels.
- Once there, select Organic, and choose Landing Page View.
- If you find some poor performers, then it would most likely be because one of these reasons:
- A mismatch between what’s promised by a search snippet and actual content on the page. In this case, a user visits your page with false expectations and leaves as soon as they aren’t met.
- A lack of internal linking. You’ve missed an opportunity to make your page a part of the sales funnel and now it’s a dead-end, which a visitor has no choice but to leave.
- Your content is of poor quality and/or looks unappealing.
6. Link Building Metrics
Backlinks are a major ranking factor and a healthy backlink profile is crucial for gaining better search positions. So, the more links you earn, the better, right? Not exactly. Gaining low-quality links, you will not only fail to improve your site authority but even hurt your website rankings.
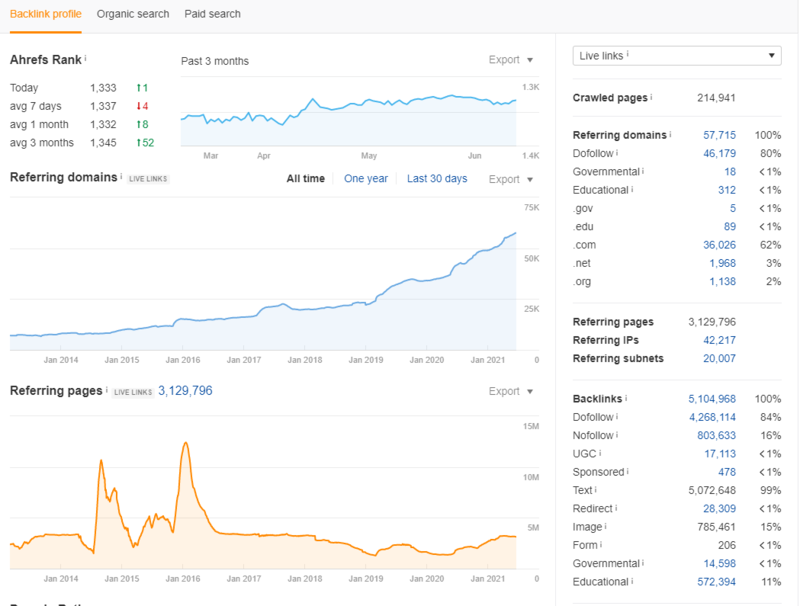
To ensure you’re building a quality link profile, it’s essential to track backlinks metrics. The link metrics that you should be measuring are:
- Total number of backlinks
- Total number of referring domains
- Number links lost
- Number of links earned
- Number of .Gov and .EDU Links
- % of Exact Match Anchor Text
- Toxic links
How to Track it
You’ll need backlink checker and analysis tools for this purpose.
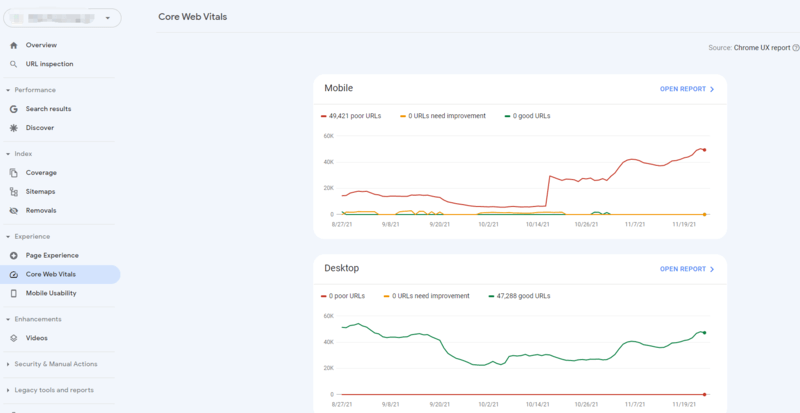
7. Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals have recently been introduced by Google as the latest user experience metrics and ranking factors. Core Web Vitals not only improve your organic rankings, but it provides your audience with a superior experience which will translates into more engaged customers, higher conversion rates, and potentially other positive benefits.
How to Track it
- Log into your Google Search Console dashboard and go to Experience > Core Web Vitals.
- The report tracks technical issues over time, so it should be fairly easy to figure out which website changes have caused the problem. If not, the report comes with a list of all discovered issues at the bottom of the page.
8. Index Status
This is perhaps the most overlooked SEO KPI.
website indexing is a process search engines use to comprehend the function of your website and each page on that website. It helps Google find your website, add it to its index, associate each page with searched topics, return this site on search engine results pages (SERPs), and ultimately drive the right people to your content.
Then, the index status of your website helps you better understand the URLs that Google (and other search engines) has indexed or has tried to do so. By tracking this SEO KPI you can pinpoint any indexing issues and figure out what caused them.
How to Track it
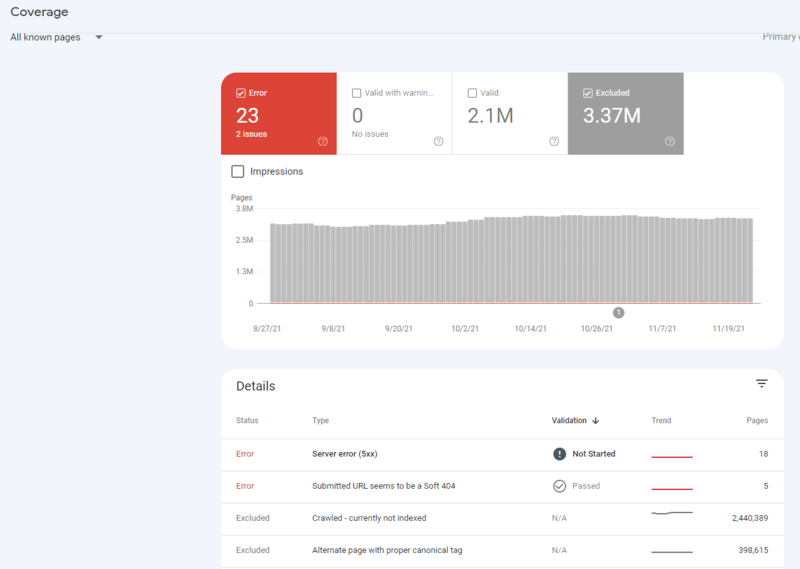
To access this data in Google Search Console and navigate to the Index tab and there you can track your Coverage and submit Sitemaps.
The “Coverage” reported issues break down in four statuses:
Valid: pages that have been indexed.
Valid with warnings: pages that have been indexed, but which contain some issues you may want to look at.
Excluded: pages that weren’t indexed because search engines picked up clear signals they shouldn’t index them.
Error: pages that couldn’t be indexed for some reason.
You can click through to various pages to see why they weren’t indexed and potentially fix any issues.
9. Leads/Conversions
Another most important KPI for SEO is measuring conversions or leads obtained from organic channels. More than any other metric, conversions is the goal so conversions are what you should track. It makes reporting on the ROI of SEO much easier.
To accomplish this, marketers must create goals (often using Google Analytics or Tag Manager) that have a defined monetary value.
For eCommerce or subscription based businesses, applying a dollar value to a successful conversion is usually pretty straightforward. In these cases, the goal is triggered on a confirmation page that follows a purchase. For B2B or service-based businesses, you often measure qualified leads rather that direct sales. Qualified leads can come from a variety of sources; including contact forms, eBook downloads, or even phone calls made after visiting the site.
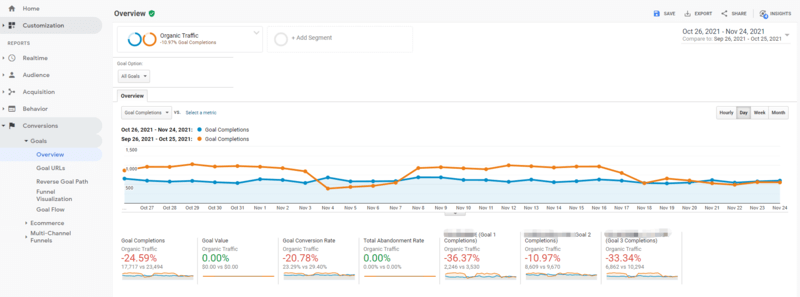
How to Track it
Log into your Google Analytics dashboard and navigate to Conversions > Overview. Then, you can check the overview of the conversions.
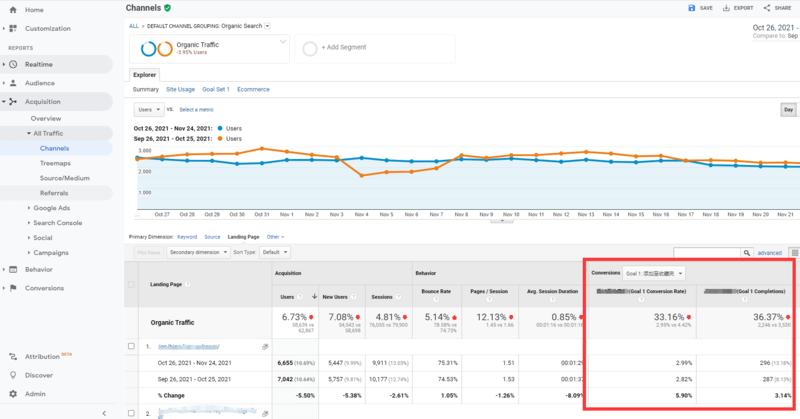
If you want to track the conversions of a specific page, select Acquisition from the left-hand menu, and then choose All Traffic > Channels. Once there, select Organic, and choose Landing Page View.
10. ROI
Finally, and progressing from the last point around conversions, you’ll want to understand if all of your SEO efforts are bringing you a solid ROI. In short, is your SEO making you more money than you’re spending on it?
How to Track it
- Calculate your SEO investment
- Track and analysis conversions
- Calculate your return on investment – (Value of Conversions – Cost of Investment) / Cost of Investment
One you’ve determined how much revenue your SEO strategy generated during a specific time period (typically a month, a quarter or a year), you can compare that amount to your SEO investment during that time to determine your ROI.
Mind that it’s common for this parameter to be negative in the very beginning. That’s because search engine optimization is a long-term investment. Each optimization you make and each piece of content you produce has the potential to deliver benefits for years to come.
Wrapping Up
The aforementioned SEO KPIs will do a neat job informing both you, your clients or your boss about the progress of your SEO campaign.
However, as all websites and clients are different, it is important to customize your SEO KPIs according to their unique needs, as well as according to the type of campaign you are running.
Here are the examples of different KPIs and metrics you need to track for different websites.
| Website type | Business goal | SEO metrics |
| Ecommerce | Increase sales | Organic search traffic on target pages Conversion rate Number of leads Transactions Positions for product keywords |
| Business (corporate) website | Increase brand awareness | Traffic to the main page Number of branded keywords (their search volume) Direct traffic Natural backlinks (mentions) Referral traffic SERP impressions |
| Business directory | Get more signups | Number of leads Organic traffic to the landing pages Bounce rate Average session duration Number of pages per session |
| Blog (personal website) | Get more subscribers | Keyword positions Organic traffic Quality backlinks Referral traffic CTR (click-through rate) Bounce rate |
| Website review (affiliate) | Get more visits | Positions for high-volume keywords Traffic Number of pages per session Number of pages that get organic traffic Number of backlinks Referral traffic |
| News websites | Get more readers | Organic traffic Number of pages that get organic traffic Bounce rate Exit pages New vs returning visitors Average session duration Number of pages per visit |