Japanese SEO Best Practices: How to Rank High in Japan
Japan has a population of 125 million and a per capita GDP of over 40,000 US dollars. After establishing an English website, many companies consider launching Japanese websites to expand their customer base.
Although the basic principles of Google SEO apply regardless of where your target customers are, many brands fail to localize their approach when entering the Japanese market – leading to poor SERP performance and ineffective keyword targeting strategies.
Based on this situation, I decided to explore some best practices for Japanese SEO.

Contents
- Japanese Internet Users
- 15 Best Practices for Japanese SEO
- 1. Use Japanese
- 2. Optimize Top-Level Domain
- 3. Hosting Server Location: Use Japanese Servers
- 4. Search Engines: Google and Yahoo! Japan
- 5. Japanese Website Design Style
- 6. Choose Japanese SEO Keywords Carefully
- 7. On-Page Optimization
- 8. URLs
- 9. Word Count: Longer is Better, But It Depends on the Content
- 10. Develop a Japan-Specific Content Strategy
- 11. Focus on Japan Backlinks
- 12. Use hreflang Tags
- 13. Mobile SEO optimization
- 14. Integrate Content and Promotion Resources
- 15. Track your results and develop improvement plans
- Conclusion
Japanese Internet Users
When studying Japanese SEO strategies, we need to first understand some basic information about Japanese internet users, such as what search engines do they frequently use? What devices do they use for searching? What are their most commonly used social media platforms?
1. Japanese Search Engines
As of December 2022, Google became the most popular mobile search engine in Japan with a 76.93% market share. It is followed by Yahoo, which accounts for approximately 14.52% of the mobile search engine market. Therefore, Google and Yahoo! Japan are the two most popular search engines in Japan.
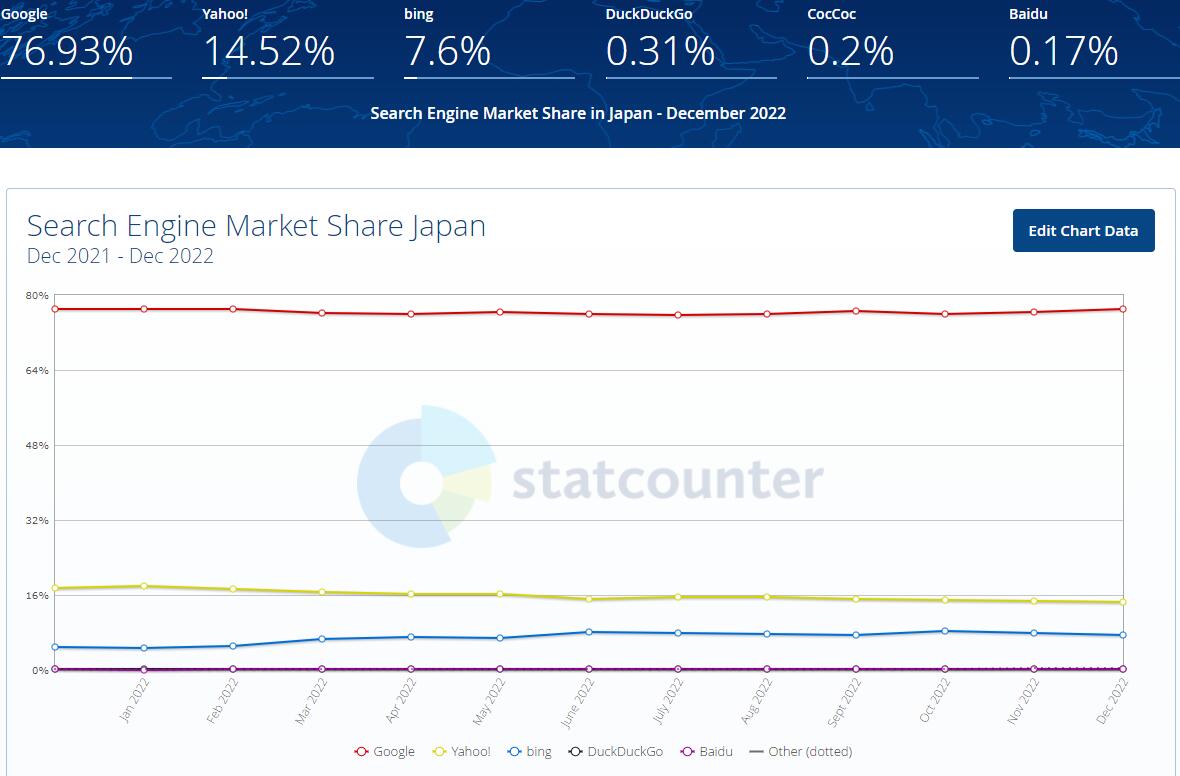
2. What Devices Do Japanese Internet Users Use to Browse the Web?
Like other countries of the world, the number of users browsing the web with mobile devices in Japan is continuously increasing. However, according to data from We Are Social, more than half (57.69%) of Japanese website traffic still comes from desktop computers, while only 39.54% comes from mobile devices. It is worth noting that the device share of website traffic may vary greatly depending on the industry. Here, we only discuss the overall situation.
This may differ from our impression – after all, we have emphasized mobile-first for many years, and it feels like everyone has a mobile phone in our daily lives.
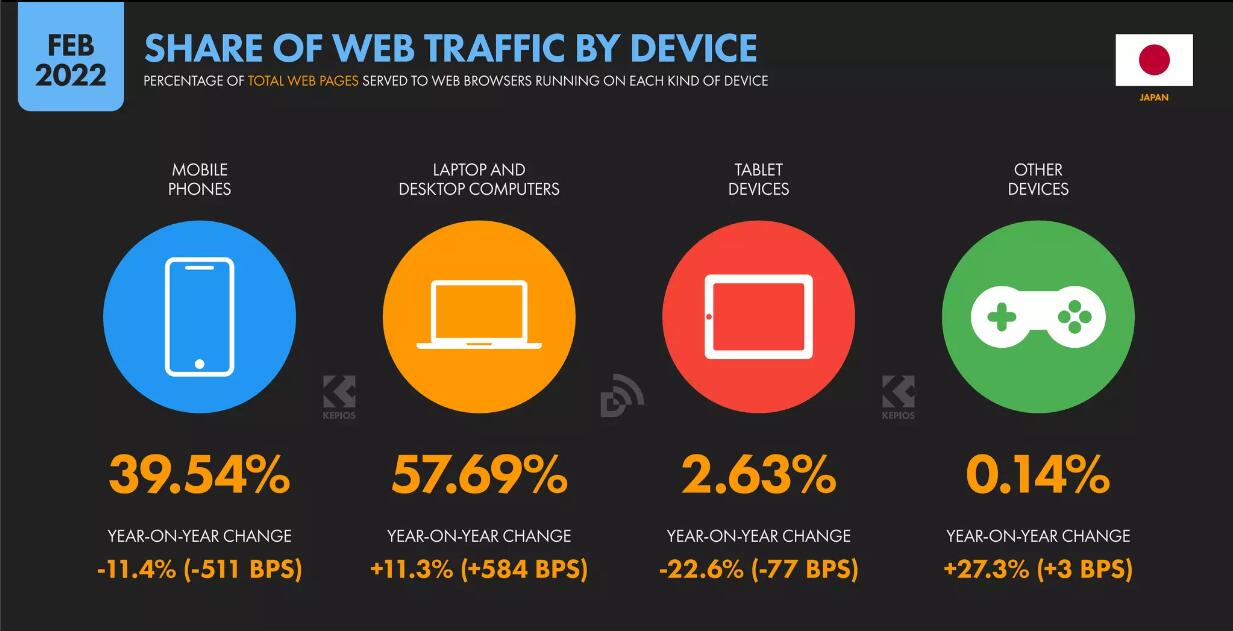
When planning SEO for Japanese websites, we also need to consider how to promote on social platforms and gain more traffic from social platforms.
According to DataReportal data, as of February 2022, YouTube ranks as the most popular social media platform in Japan with an 81% penetration rate. In addition, the most popular local social media in Japan is Line, with approximately 79.6% of Japanese users on this platform. Moreover, Twitter (58.2%) and Instagram (47.7%) are also popular in Japan. Please note that only 30.8% of Japanese users use Facebook – this platform is not particularly popular among Japanese people.
15 Best Practices for Japanese SEO
1. Use Japanese
If you decide to do Japanese SEO, you definitely need Japanese content first. Note that you should ensure that your content quality is satisfactory, as translation may not be enough – you need to consider cultural differences.
2. Optimize Top-Level Domain
When hosting a Japanese website, you should consider two different Japanese top-level domains – .co.jp and .jp. “.co.jp” is reserved specifically for companies registered in Japan. Therefore, for domestic companies, the ccTLD (country code top-level domain) – domains ending with .jp in Japan – is often the first choice, as it does not require registering a company in Japan but can still win the trust of Japanese users and usually rank higher in Japanese searches.
Here are some examples ending with “.jp” or “co.jp”.
- https://www.softbank.jp/
- https://www.rakuten.co.jp/
- https://www.sony.jp/
If you are already a global company with a large number of high-quality backlinks and traffic directed to your .com domain, I recommend creating a separate subfolder for Japan, such as www.example.com/ja/, so you can continue to benefit from the domain authority and links of the original site.
3. Hosting Server Location: Use Japanese Servers
Server location is the country where the server is located, and Google can determine the server’s location (country) from the IP address. According to Google Search Central’s official documentation, server location seems to also affect search results.
” In our understanding of web content, Google considers both the IP address and the top-level domain (for example, .com, .co.uk).”
“ In the absence of a significant top-level domain, we often use the web server’s IP address as an added hint in our understanding of content.”
Therefore, if possible, it is best to use servers located in Japan or rent hosted servers.
4. Search Engines: Google and Yahoo! Japan
This best practice can save you a lot of valuable time and effort in the Japanese SEO process.
As mentioned earlier, Google and Yahoo! Japan are the two largest search engines in Japan. However, since 2010, Yahoo! Japan has been using Google’s algorithm to rank natural search results. This means that you don’t need to optimize for the two search engines separately. When you optimize for Google, you are also optimizing for Yahoo. Of course, in reality, Yahoo! and Google search results are not exactly the same. This is because both Yahoo and Google have their own unique content.
5. Japanese Website Design Style
Western users often favor a minimalist style for website design, but Japanese website design often adopts the “more is better” principle.
If you look at popular Japanese websites, you will find some characteristics. There may be some differences between different product categories, but here are some features that may stand out:
- Less white space on pages compared to typical websites in the USA or Europe
- Frequent use of cartoons, manga, or “cute” elements
- Several contrasting colors used within a small scope
- Content aims to provide information for user decision-making, rather than simply establishing emotional connections – providing a wealth of technical data and information
- Data, recommendations, and statistics are given higher priority on landing pages to build trust with users
Note: Japan’s population is aging rapidly, and the preferences of older and younger generations may differ significantly. For example, young Japanese may begin to prefer more Western-style web design aesthetics. Therefore, when implementing web design, it is necessary to understand the needs of your target audience and observe the practices of your competitors.
6. Choose Japanese SEO Keywords Carefully
Japanese has four writing systems – hiragana, katakana, kanji, and Latin alphabet. Therefore, one word can have multiple forms. For example, if a Japanese user wants to search for sushi, there are six ways to write it: “すし (sushi)”, “スシ (sushi)”, “寿司 (sushi)”, “鮨 (sushi)”, “寿し (sushi)”, and “Sushi”.
While Google’s current algorithm is smart enough to possibly consider all these as the same word, more often than not, search results may differ based on the different keywords. Moreover, even though these words have the same meaning, their search volumes are different.
7. On-Page Optimization
When it comes to on-page optimization, such as titles, meta descriptions, headings, body text, image alt text, and internal links, Japanese SEO is basically no different from how we handle it in any other country/region. The only thing we need to remember is that Japanese characters are double-byte, which affects the optimal length of titles and meta descriptions. The optimal length of titles and meta descriptions is determined by pixels, but here are some general standards:
- Title tags: Maximum title length displayed in search results is 28 characters
- Meta description tags: About 90 characters displayed on PC search results, and about 49 characters on mobile devices.
Important tip: Since Japanese consider brand reputation as an important element, consider placing your brand name at the end of the title tag. This will help increase brand awareness and signal to searchers that you have a trustworthy brand name, which will help improve the click-through rate of your webpage.
8. URLs
Since the content is written in Japanese, it seems natural to create URLs in Japanese. However, in practice, we encounter some challenges. If you visit a URL like “https://www.google.com/search?q=日本语”, if you copy and paste this URL, it will be encoded as “https://www.google.com/search?q=%E6%97%A5…”. The compiled code is sometimes long, neither easy to remember nor easy to share. In this case, you’d better use English letters in the URLs.
Anyway, using non-English URLs for non-English websites is acceptable, and Google can crawl, index, and rank them. Also, the language used in the URL has no impact on ranking. Therefore, you can choose either way according to your preference. Based on my observation, more Japanese websites use Latin characters for URLs.
9. Word Count: Longer is Better, But It Depends on the Content
Word count has no direct relationship with SEO ranking, but longer content generally provides more information to meet user needs. Therefore, when we research the top-ranking Japanese pages, we find that the average number of Japanese characters on these pages is about 4,000 to 5,000, which is equivalent to about 1,600 to 2,000 English words.
Although word count is important, writing meaningless long articles will not help you improve your ranking. If you intentionally lengthen the article or repeat some content to make it difficult to read, then from the user’s perspective, a concise and easy-to-understand article will be a better article.
10. Develop a Japan-Specific Content Strategy
When writing articles and content for your Japanese website, be sure to write content that resonates with Japanese users. My point is simple: try to create content, websites, and user experiences around Japanese people’s expectations.
In Japan, articles sharing knowledge and tips are popular. You can try to create more of this type of content.
11. Focus on Japan Backlinks
When you start your SEO strategy in Japan, focus on obtaining backlinks from Japanese websites to increase your local authority. You can use tools like Ahrefs to check what external links your Japanese competitors have and try to “steal” some if possible.
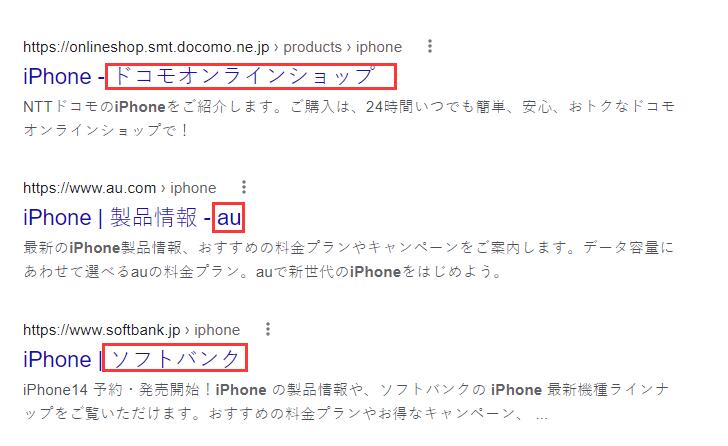
Some webmasters may find that even though they have provided a Japanese version of the content, their English global website ranks higher than their Japanese website. The reason this happens may be due to a lack of necessary hreflang tags, which prevents Google from understanding that your Japanese website is for Japanese users, and your global English website is for English users.
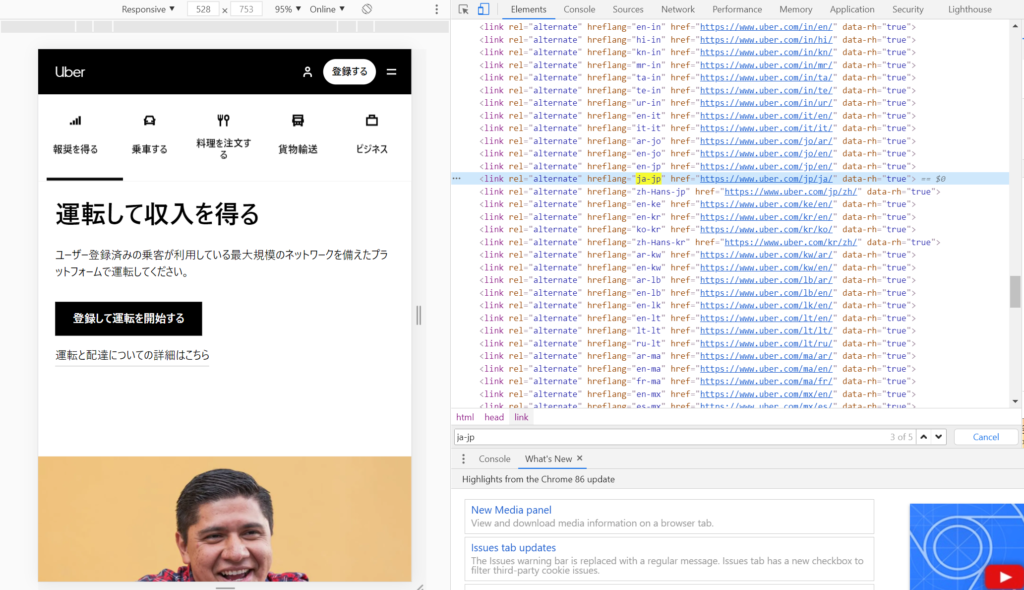
Here’s an example: This is Uber’s Japanese website. As you can see, there is a bunch of multilingual hreflang tag code written like this:
<link rel=”alternate” hreflang=”ja-jp” href=”https://www.uber.com/jp/ja/”>
This code is crucial for ensuring Google recognizes this page as the Japanese website. You need to apply this code correctly to your global website and multilingual websites.
Important tip: For SEO beginners, using hreflang tags correctly can be quite challenging. Therefore, I suggest that beginners learn some basic knowledge and work together with the technical team to add hreflangs to webpages. After the addition is completed, you can check whether the hreflang tag is added correctly in Google Search Console. Of course, some tools like Ahrefs can also discover errors through Site Audit.
13. Mobile SEO optimization
Although mobile search in Japan progresses slower than the global average, more than 40% (mobile + tablet) of website traffic still comes from mobile devices. Therefore, you need to ensure that your website is mobile-friendly. Generally, we recommend responsive web design. What is a responsive website? The design elements of the website will adjust in size according to the device, providing users with an excellent visual and browsing experience.
14. Integrate Content and Promotion Resources
Content marketing and SEO should go hand in hand. And there are many intersections between SEO, PR, PPC, email marketing, and social media, which some brands have not realized. You need to plan your projects more comprehensively and encourage teams (even if they are external agencies) to collaborate and share resources. By integrating content and promotion resources, you can save a lot of time in SEO, and the content can be reused for different promotion channels.
Important tip: Always promote your SEO content on social media channels, bringing more traffic to your content and increasing the chances of being shared. This also provides strong social proof for anyone who wants to learn more about your brand before making a purchase. As we mentioned earlier, the most popular social channels in Japan are YouTube, Line, and Twitter.
15. Track your results and develop improvement plans
When operating a website, it is essential to monitor the website’s data regularly. Here are some common data tracking items:
- Keyword rankings of your website and competitors on Google and Yahoo
- Ratio of branded searches to non-branded searches
- Overall search volume trends in your market
- High-potential keywords and topics (including those not currently included in your SEO keyword target list)
- Site visits, conversions, page views, bounce rates, average session duration, sales, etc.
- Where new users “drop off” before making a purchase or completing a potential customer form
With the feedback from the data, you can continuously optimize your SEO strategy (including keywords, content, design, etc.).
Conclusion
Since the main search engine in Japan is still Google, we can continue to adopt Google SEO best practices to optimize Japanese websites. However, some “localized” SEO issues in Japan listed in this article are also worth paying attention to, especially the selection of domain names and server locations, which need to be “made right” from the beginning. Otherwise, you will waste time and costs for no reason.
The Japanese SEO best practices listed in this article may not be exhaustive, but they should provide some insights for Japanese SEO newcomers and serve as a good starting point.