What is Google Analytics 4 (GA4): Getting Started with GA4
As an online marketer or a SEO analyst, you must have used Google Analytics. Google Analytics provides simple but comprehensive data of our websites which allow us to find out how our websites run and how users integrate with our websites.
Then, in October 2020, Google launched a new generation of analysis tool – Google Analytics 4 (GA4).
What is Google Analytics 4? What are the differences between Universal Analytics and Google Analytics 4? And most importantly, how Google Analytics 4 can help us increase the traffic of our website?
Today, I’ll walk you through the setup of GA4, discuss the difference between Google Analytics and GA4, analyze whether it is necessary to install GA4, and finally the how the use GA4.
Ready to learn more? Let’s get to know Google Analytics 4!
Contents
What is Google Analytics 4?
Google Analytics 4 has been in development since the initial release of “Google Analytics for Firebase” back in 2017, and a beta version was released in July 2019 under the name “App + Web Properties”.
Google announced Google Analytics 4 in October 2020.
Google Analytics 4 or GA4 is the next evolution of analytics tracking and was built to understand how users are engaging with your brand across all platforms and devices. Google self-describes Google Analytics 4 as a next generation approach to “privacy-first” tracking, x-channel measurement, and AI based predictive data all at once.
All in all, GA4 is a completely new system that is totally separate from Universal Analytics (often referred to as simply “Google Analytics”).
In the following paragraphs, I’ll explain how it differs from Universal Analytics.
What Are the Differences Between Universal Analytics and Google Analytics 4?
The new Google Analytics 4 comes with a bunch of key features that make it very different from the old version. And, there are five major differences between UA and GA4.
1. Web and App Tracking Combined in GA4
First of all, GA4 simplifies the process of getting a full funnel view of what’s happening on your site and apps. This new web + app user tracking will give you the ability to compare and understand how users are engaging across both your website and mobile app.
2. Data Is Tracked by Events, Not Sessions
Another big difference is how users are tracked.
In Universal Analytics, users are tracked via sessions, and these sessions are the foundation of all reporting. During a session, Analytics collects and stores user interactions, such as pageviews, events, and hits. A single session can contain multiple hits, depending on how a user interacts with your website.”
However, GA4 is event based. Instead of creating a new session when a user enters to a site, GA4 records all events they complete. This allows Google to more accurately de-duplicate users and emphasizes what users actually do on your site.
For more details, see Google’s help center article: Universal Analytics versus Google Analytics 4 data.
3. Engagement Rate Replaces Bounce Rate in Google Analytics 4
Because Google Analytics 4 uses an event-based model rather than a page-view model, certain page-level metrics such as Bounce Rate will be going away moving forward.
Instead, GA 4 will rely on Engagement metrics which represent metrics like user’s engagement on a single page and events on a subsequent screen or page, over a duration of time.
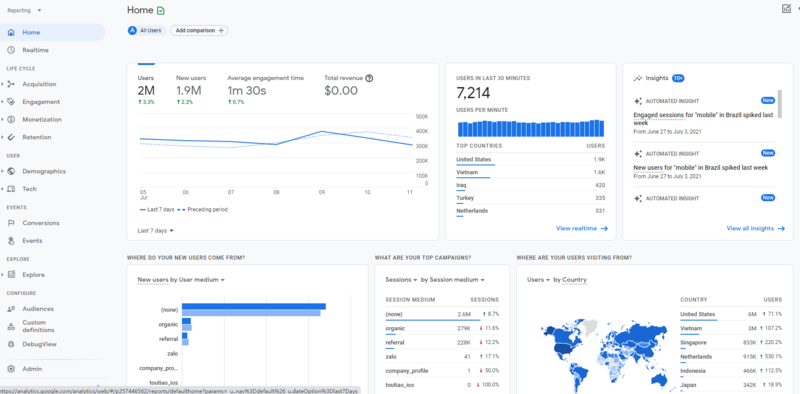
4. Customer Lifecycle-Framed Reporting
The user flow report in Google Analytics has been a pain point for many Universal Analytics users. With GA4, reports work similarly to what you would find in Google Data Studio and bring a much more robust reporting capability for user flows and journeys.
GA4 organizes data by customer lifecycle – acquisition, engagement, monetization, and retention. It’s more focused on measuring an end-to-end user journey and not just individual metrics across devices, pages, or channels. This journey is now a staple of any viable marketing strategy.
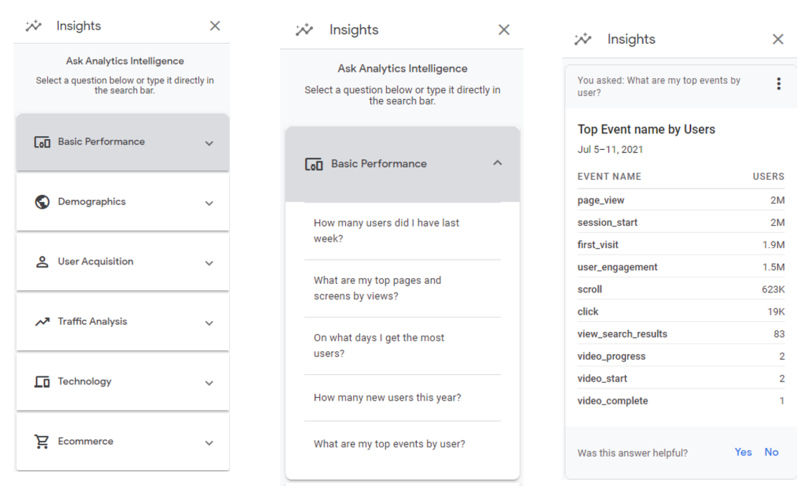
5. New AI-powered Insights and Predictive Metrics
Based on your data, GA 4 will now give you personalized insights and analysis based on past trends and future predictions. You will have the ability to ask custom questions and review suggestions made by Google’s AI algorithms.
It will also give you AI-driven date comparisons that will help marketers better manage budgets and traffic allocations.
How to Set-Up Google Analytics 4?
For Users Create a New Analytics Property
As part of the push to encourage users to transition to Google Analytics 4, when a user creates a new Analytics property, Google’s default option will be a new GA4 property.
Step #1. Go to analytics.google.com and hit the blue “Create Property” button in the Admin section.
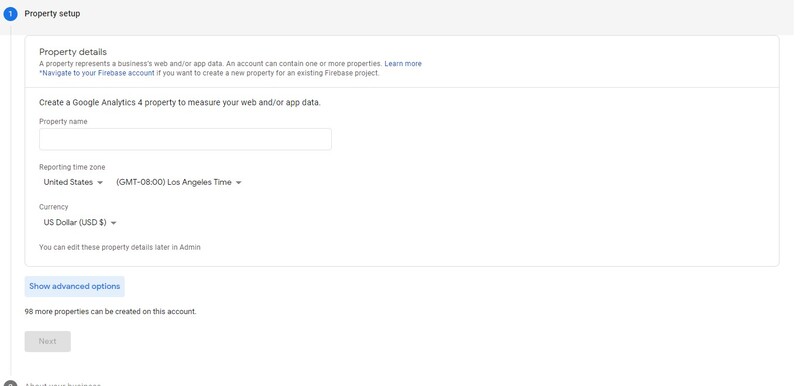
Step #2. Give your property a name and select your reporting time zone and currency as shown below.
Note: If you want to create a Universal Analytics property, you can do so by hitting the “Show advanced options” button below.
Step #3. Create a “data stream”. A data stream is a new term for GA4 and refers to the app type (iOS or Android) or whether it is a website.
Step #4. Enable data collection by placing the GA4 tracking code on your website or app. Placing the javascript code can be done directly on the site or through Google Tag Manager.
Step #5. Add “Recommended Events” to your data stream.
For Users Who Have an Existing Analytics Account
For uses who have an existing analytics account, there is no reason to panic to set up GA 4. Your existing Universal Analytics setup will continue to work — Google is not sunsetting this product in the foreseeable future. However, all new properties and all product development & enhancements will be made in Google Analytics 4 (and not in Universal Analytics).
Therefore, we recommend that you create a GA 4 property ASAP to run in parallel with your existing Universal Analytics setup.
Here’s how to upgrade to GA4.
Step #1. Navigate to your Admin Settings within your Google Analytics Account. Under Property Settings, look for the ‘Upgrade to GA4’ link.
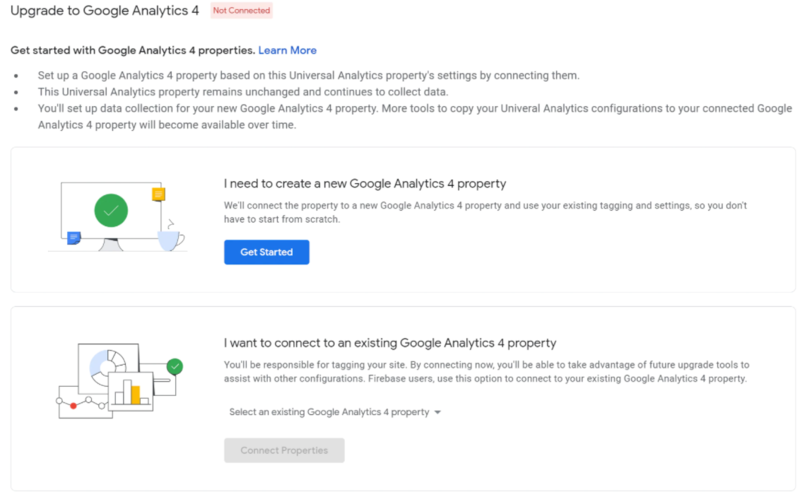
Step #2. Click ‘Get Started’ to begin the setup process with Google Analytics’ setup wizard. Then you’ll have several options depending on your current GA setup.
Step #3. In order to start the data collection, we’ll need to generate a Measurement ID for our new GA4 Property. The Measurement ID is similar to the UA ID.
Step #4. Configure your Data Stream by entering your Website URL and Stream name. Click ‘Create Stream’ when finished.
Step #5. Customize event measurement, activate Google signals, set up conversions and so on.
Step #6. Once you’ve got the tag configured, check your property to ensure it’s collecting data correctly. You can do this by visiting your site, then opening your new GA4 property and navigating to “Realtime.” You should be able to see a visit from your geographic region.
Takeaways
Google Analytics 4 is certainly a very exciting development for the industry.With improved predictions and customer insights from AI, and better integrations with marketing platforms, such as Google Ads, Google Analytics 4 provides marketers with a more complete cross-channel view of your customer journey and future customer behaviors.
However, GA4 is a very different experience for users who are familiar with Universal Analytics. A switch to GA4 will require changes to implementation, tracking and time investment within the platform. For me, it is a bit difficult to learn how to use GA4.
All in all, I strongly recommend that you begin a roadmap to implement GA4 in 2021 while keeping their Universal Analytics implementation alive.