How to Remove Unwanted Results from Google Search (6 Ways)
Sometimes you may want to remove some search results from Google search.
For example, if you just deleted a page and don’t want it to show up anymore. Or if you want to remove low-quality pages from the index for SEO reasons.
For ORM (online reputation management) reasons, you may want to remove incorrect, problematic, or outdated info about you or your business online. Otherwise, they can hurt your reputation.
Fortunately, there are many ways to remove results from Google, but there’s no one size fits all approach. It all depends on your circumstances.
In this post, we’ll discuss 6 different ways to remove results from Google. They are mainly divided in 2 parts – remove web pages from your own website and remove unwanted results from the website you don’t own.
Here we go.
Contents
Part 1: How to Remove Your Website or Web Page from Google
It is easy to delete a search result if you control the website that contains the information. Here I’ll introduce 3 ways.
Method 1: Temporary Removal Using Google Search Console Removals Tool
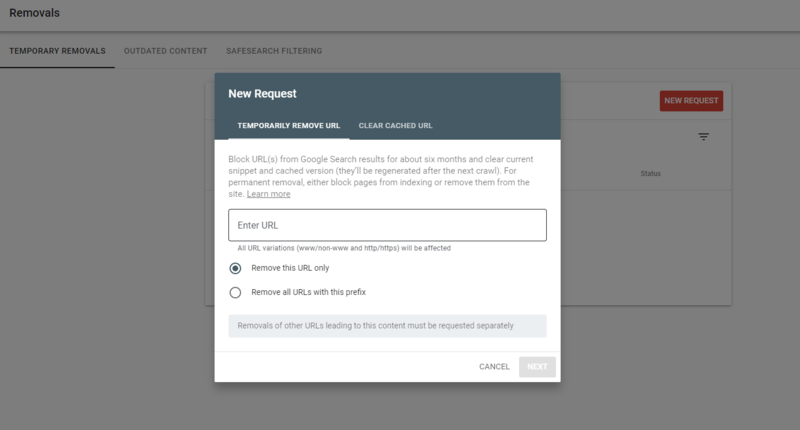
It’s easy to remove URLs belonging to a website you own using Google Search Console. Follow the steps below to remove a URL from Google Search.
Step #1. Visit the Remove URLs tool here: https://www.google.com/webmasters/tools/url-removal
Step #2. elect your website under “Please select a property”
Step #3. Click the grey button, enter your URL and click “Continue”
Step #4. Click “Submit Request”
When to use Google Search Console
- You have a URL on a Search Console property that you own, and you need to take it off Google Search quickly.
- You’ve updated the page to remove sensitive content, and want Google to reflect the change in Search results.
Note: The Removals tool enables you to temporarily block pages from Google Search results on sites that you own. You must take additional steps to remove the URL permanently. The URL to remove can be for a web page or an image.
To permanently remove a URL, use method #2 or #3.
Noindex tags are a directive which tells Google “I do not want this page to be indexed and therefore do not want it to appear in the search results.”
When Google next crawls that page and sees the noindex directives, it will remove that page from its index and therefore the search results.
These noindex tags can be implemented in two ways:
- By including them in the page’s HTML code
- By returning a noindex header in the HTTP request.
Noindex tags implemented in the HTML would look something like this:
<meta name=”robots” content=”noindex”>
Noindex tags implemented via HTTP header would look like this:
HTTP/… 200 OK
…
X-Robots-Tag: noindex
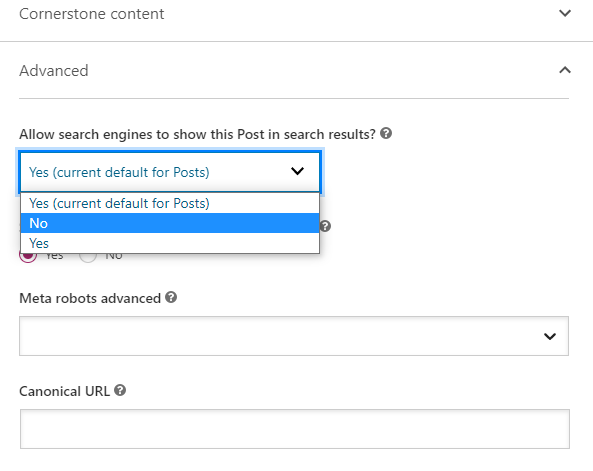
If you use a content management system like WordPress, then the Yoast SEO plugin provides options to noindex individual posts and pages. In this case, you don’t need the coding knowledge.
Under Advance > “Allow search engines to show this Post in the search results?” — change from “Default” to “No” — this will add the noindex meta tag to the head section.
When to Use Noindex Tags?
If there are pages on your site that still serve a purpose, but you do not want to appear in the search results this is a good option.
Method 3: Deleting the Page
The most obvious answer, you may have thought, would be to simply delete the page whether that’s by giving it a 404 or a 410 status code.
Googlebot will try to crawl the URL again soon and remove it from the index when it sees the 404 or 410 error.
However, from an SEO perspective, if these deleted pages hold value, whether that be through backlinks or traffic, it would be worth 301 redirecting to a relevant page in order to consolidate that link equity on the site.
When to Delete a Page
If the page serves no purpose and has little value in terms of backlinks or traffic it may be worth deleting. If there is some value either from a user perspective or an SEO perspective, consider keeping it with a noindex tag or 301 redirecting to a relevant page.
Part 2: How to Remove Results from Sites You Don’t Own
It is much harder to remove search results from Google if they don’t belong to a site that you control.
It makes sense that we cannot delete others’ content arbitrarily. However, some content in the website may:
- Harm your personal reputation and relationships;
- Harm your business or professional reputation;
- Cause stress and be emotionally taxing to you personally;
- Cost you a great deal of money (either by losing customers or employment).
In these cases, we have to remove the results from Google and even other search engine.
Here, I listed 3 ways to remove unwanted results from sites you don’t own.
Method 1: Contact the Webmaster Directly
Usually, you can easily find the contact information of a website. However, in my experience a webmaster will often not remove online content. After all, they write and publish the post for ranking and traffic. But, sometimes they will.
You need to think again whether contacting the webmaster will make things better or worse before contacting. There are two common cases:
- Some people or companies ask attorneys to send a legal demand letter to a webmaster in order to scare them and then delete the content. However, some webmaster will simply add the “letter” to the original page and then many more people comment on it.
- Some may ask a webmaster to delete a page by giving them benefits. Yes, they delete a page and then write and publish more similar pages for more benefits.
Think twice before contacting the webmaster.
If you decide to contact the webmaster and he/she agree to delete the page related to you, then you can ask them follow the methods introduced in part 1 to delete the page.
Method 2: Ask Google to Remove Unwanted Result by Sending DMCA Takedown Request
This method can only be used when someone has copied your content.
Sometimes, we found someone copied the content from our website and rank higher than ourselves. In this case, you can ask Google to takedown the copied content.
Here’s how to do it.
Step #1. Go to https://support.google.com/legal/troubleshooter/1114905?hl=en
Step #2. Choose what Google product does your request relate to. Here we choose “Google Search” as an example.
Step #3. Choose “Intellectual property issue” > “Copyright infringement”.
Step #4. Create your request by filling the form.
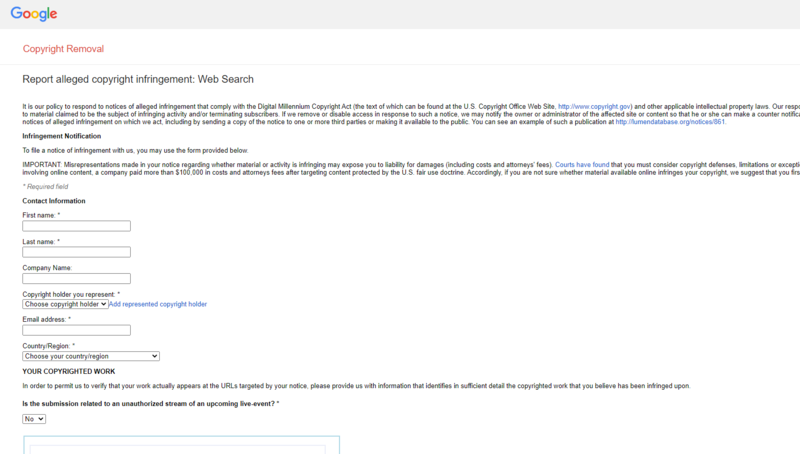
Step #5. Once you submit the DMCA complaint, Google will review it and follow up with some actions. It takes up to 10 days in our experience for Google to accept or reject the request.
However, keep in mind that if Google does take action, they can only remove the content from their search results. That content is still present on the original web page (and on Bing and other search engines).
In similar ways, you can report malware or phishing website to Google. You can also ask Google to remove personal information (personally identifiable information, doxxing, non-consensual explicit imagery, etc.).
Method 3: Complain to Hosting to Remove Search Results
Like Google, you can report malware or phishing websites to their web hosting. Also, If you find a site that is hosting content you’ve created but without your permission, you can report it to its web hosting company too.
Here we take “copyright infringement” as an example to show you how to submit a DMCA takedown request to web hosting company.
Step #1: Take screenshots of the infringing site
Step #2: Locate the website’s host with Hosting Checker
Step #3: Determine the copyright agent. You need to determine the exact person to send your notice to. Legally this person is called the Copyright Agent. Often the best way to determine this is to Google the web host. Once on the web host’s site, the Copyright Agent can be found by:
- Clicking “Legal” or “Terms of Use” (often in the footer)
- Selecting something like: “Copyright”, “Notice for Claims of Copyright Violations”, or “Agent for Notice”
Step #4: Draft your takedown notice. By law, the DMCA Takedown Notice must contain the following items:
- A physical or electronic signature of a person authorized to act on behalf of the owner of the copyright or intellectual property right that has been allegedly infringed upon;
- Identification in sufficient detail of the material being infringed upon;
- Identification of the material that is claimed to be infringing upon the intellectual property. Include information regarding the location of the infringing material with sufficient detail so that the web host is capable of finding and verifying its existence;
- Contact information about the notifier including the name of the intellectual property owner, the name and title of the person contacting the web host on the owner’s behalf, the address, telephone number and, if available, e-mail address;
- A statement that the notifier has a good faith belief that the material is not authorized by the intellectual property or copyright owner, its agent, or the law; and
- A statement made under penalty of perjury that the information provided is accurate and the notifying party is authorized to make the complaint on behalf of the intellectual property or copyright owner.
Some hosting providers may have DMCA takedown requests that you can file on their site. You can check for this before you draft and mail the letter.
Step #5. If your request is found to be valid, the hosting provider can remove or disable access to the infringing content.
Final Thoughts…
There you have it — different methods for removing results from Google that serve differential purposes.
You now know how to remove URLs temporarily from Google search and permanently. Also, you know how to remove web pages on your website and those out of your control.
If you have other questions, please leave your comments below.